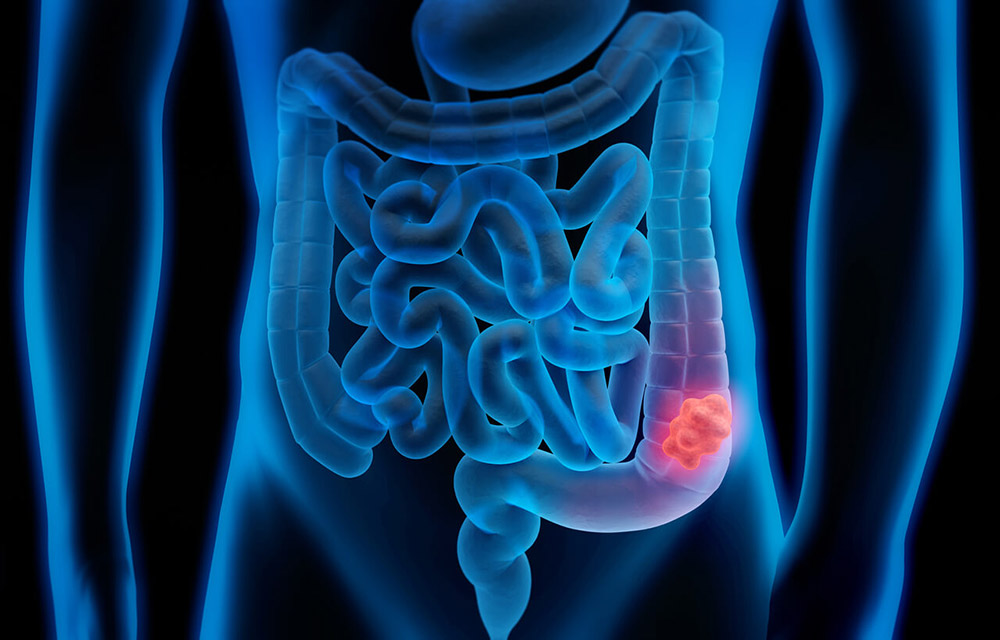
WHAT IS COLORECTAL CANCER?
Colorectal cancer or colon cancer is a cancer that occurs in the colon or rectum. The colon is the colon while the rectum is the part that connects the colon and the anus. Colorectal cancer occurs frequently in the world. The risk of developing colon cancer increases as age increases. It is usually found among those aged 50 or older. In the early stages, colorectal cancer may have no symptoms. It usually starts with polyps (radius -shaped projections) in the colon that then turns into cancer. Screening tests are important for early detection of colorectal cancer. If colorectal cancer can be detected early, the opportunity to recover is good.
- Age: Over 90% of cases in Malaysia occur at over 40.Polyps: Adenoma type polyps can cause cancer.
- Intestinal inflammation: such as “ulcerative colitis” and “crohn’s disease” (intestinal, intestinal and wounds) form a long -standing inflammation.
- Cancer History: Women with ovarian, uterine or breast cancer are likely to have colon and rectal cancer.
- Family History of Cancer: Family members get colon and rectal cancer, especially when cancer is found at the age of 60.
- Nutrition: High fat foods and lack of fiber.
- Smoking: Studies show more smokers die from colon and rectal cancer than non -smoking individuals.
- Non -steroidal painkillers: Examples of aspirin can reduce the risk of colon and rectal cancer formation as a result of some studies.
- Food and medicine: Foods rich in fruits, vegetables and less red meat may reduce the risk of colon and anal cancer. Some studies have found that consuming folic acid and calcium can reduce the risk of colon and rectal cancer.
- Weight and physical activity: Individuals with inactive lifestyle and individuals are overweight or obesity increases the risk of colon and rectal cancer.
- If you or your immediate family have a colorectal polyp or colorectal cancer.
- If you have intestinal inflammation such as ‘ulcerative colitis’ and ‘Crohn’s Disease’
- If you have cancer-related genetic syndrome such as ‘Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)’ or ‘Hereditary Non-Polyposis Colorectal Cancer’
SIGNS OF COLORECTAL CANCER
- The abdomen is uncomfortable, including frequent bloating, cramps and seizures.
- Lose weight for no reason
- Frequently tired or tired
- Changes in impurities dumping habitat.
- Diarrhea, constipation or intestinal feelings cannot be completely emptied.
- The stool is red or too dark in the stool.
- The stools look small in size or flush from normal.
SOURCES: MyHealth Malaysia Official Portal